Ganga River System
River Description
- It Originates from the Gangotri glacier of western Himalayas in the state of Uttarakhand.
- It flows through India and Bangladesh and then reaches Bay Of Bengal.
- The Ganga basin outspreads in India, Tibet (China), Nepal and Bangladesh over an area of 10,86,000 Sq.km.
- In India, it covers states of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, West Bengal, Uttarakhand, Jharkhand, Haryana, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh and Union Territory of Delhi draining an area of 8,61,452 Sq.km which is nearly 26% of the total geographical area of the country.
- The basin is bounded by the Himalayas on the north, by the Aravalli on the west, by the Vindhyas and Chhotanagpur plateau on the south and by the Brahmaputra Ridge on the east.
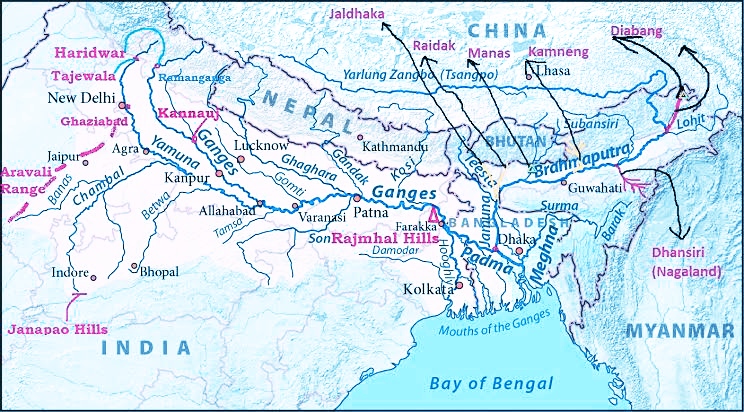
Fig : Ganga River Basin
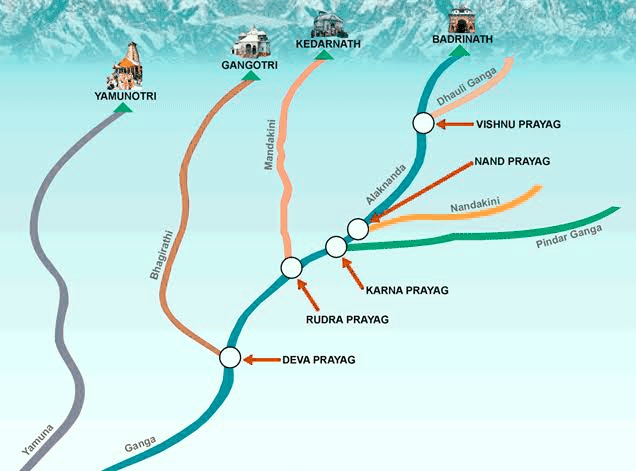
- At its source, the river is called as the Bhagirathi.
- It descends down the valley upto Devprayag where after joining another hill stream Alaknanda, it is called Ganga.
- The Ganga originates as Bhagirathi from the Gangotri glaciers in the Himalayas at an elevation of about 7010m in Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand and flows for a total length of about 2525 km up to its outfall into the Bay of Bengal through the former main course of Bhagirathi-Hooghly.
- The principal tributaries joining the river are the Yamuna, the Ramganga, the Ghaghra, the Gandak, the Burhi Gandak, the Kosi, the Mahananda and the Sone. Chambal and Betwa are also the two other important sub-tributaries.
- There are number of industrial centres located in the sub-basin such as Faridabad, Ghaziabad, Kanpur, Dhanbad, Durgapur etc.,
Panch Prayag in Himalayas :
Soil Types
Predominant soil types found in the basin are sand, loam, clay and their combinations, such as sandy loam, loam, silty clay loam and loamy sand soils.
Topography
- The Ganga and its tributaries have formed a large flat and fertile plain in North India.
- The availabilities of abundant water resources, fertile soil, and suitable climate have given rise to a highly developed agriculture based civilization and one of the most densely populated regions of the world.
- The net sown area in the Ganga basin in India is around 44 million hectares (M-ha) and the net irrigated area is 23.41 M-ha.
- Migration of the tributaries draining the eastern part of the basin has resulted in conspicuous back-swamp and meander bolt deposits.
- These sedimentological features play a dominant role in the hydrodynamics of the region.
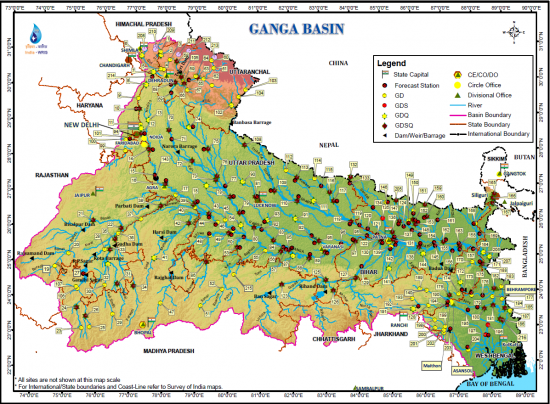
Fig : Ganga Basin .Source : WRIS
Tributaries
Left Tributaries
1.Ramganga
2.Garra
3.Gomti
4.Ghaghara
5.Gandak
6.Burhi Gandak
7.Koshi
8.Mahananda
Right Tributaries
1.Yamuna
2.Tamsa
3.Sone
4.Punpun
5.Falgu
6.Kiul
7.Karamnasa
8.Chandan
9.Ajoy
10.Damodar
11.Rupnarayan
Tributaries Explanation
Left Bank
1.Ramganga

Fig : Corbett National park
- It originates from Doodhatoli ranges at namik Glacier in the state of Uttarakhand.
- It flows through Corbett National park .
- It flows through Bareilly district of Uttar Pradesh .
- It joins Ganges near Kannauj.
2.Garra River .
- It flows through the industrial area of shahjahanpur district of Uttar Pradesh.
- This river has faced water quality problems due to the industrial development and urban growth along the river.
3.Gomti or Gomati River
- This river originates from Gomat Taal near Pilibhit in th state of Uttar Pradesh.
- It has number of tributaries that join this river before it’s confluence with Ganges.
- The Markandey Mahadeo temple is at the confluence of th Gomti and the Ganges.
- This river meanders through the Lucknow city.
- This river also faces pollution problem due to the industrial development.
3.Ghaghara or Karnali river.
- It originates in Mapchachungo Glacier in Tibetian plateau near Lake Manasarovar.
- It cuts through the Himalayas in Nepal and Joins Sharda river at Brahmaghat in India.
- It joins Ganges in the state of Patna .
- This river is also known as Sarayu river.
- It’s tributaries are Bheri, Chhoti Gandak,Rapti,Seti,Budhi Ganga etc..
4.Gandak River

- This river is also known as Narayani River.
- It originates in Nhubine Himal Glacier in Nepal.
- This river flows through a gorge between the mountains Dhaulagiri and Annapurna.
- This river is older than Himalayas.
- It then confluence with Ganges in the state of Bihar.
- Valmiki National Park is located near to Gandak River.
5.Burhi Gandak River
This river originates from Chautarwa Chaur in the state of West Bengal.
6.Koshi River
- It is also known as Saptakoshi for its seven upper tributaries.
- It originates at Triveni in Nepal.
- It carries heavy silt during rainy season and causes extreme floods.
- So this river is also known as ” Sorrow of Bihar “
- It joins with Ganges in the state of Bihar.
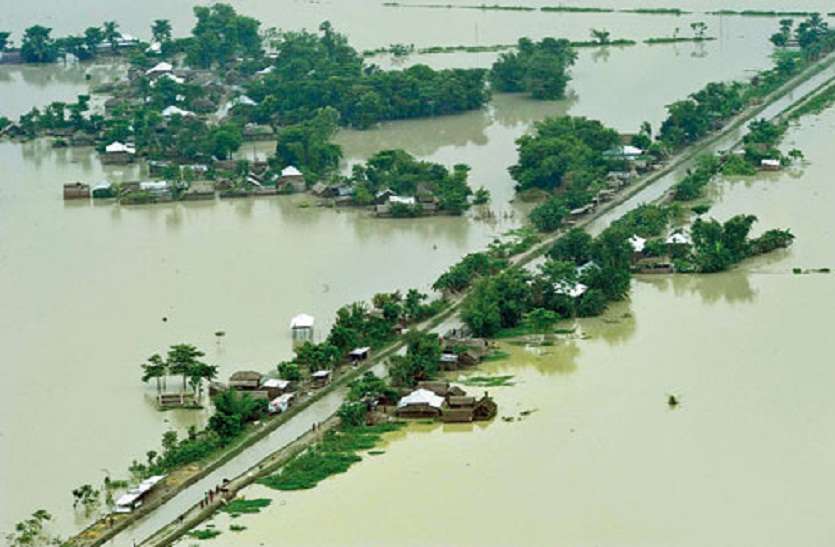

Fig : Koshi Flood in Bihar
7.Mahananda River
- It flows through Bihar and West Bengal in India.
- It originates in Paglajhora Falls on Mahaldiram Hill in the Darjeeling district.
- It joins with Ganges in Bangladesh .
- This river flows through Siliguri Corridor which is the Gate way of North East India.
Right bank tributaries.
1.Yamuna
- It originates from the yamunotri glacier Near to Banderpooch peaks in the state of Uttarakhand.
- It merges with Ganges at prayagraj ,which is a site of Kumbh Mela , a Hindu festival held every 12 years.
- Yamuna river will be discussed in seperate topic..
2.Tamsa River
- Also called Tons river .
- It flows through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- It Originates from Tamarkund in Kaimur Range in the state of Madhya Pradesh.
- It flows through Rewa Plateau in Madhya Pradesh .
- Purwa falls is located in this river .
3.Son river .
- It Originates from Amarkantak ,just near to Narmada River in the state of Madhya Pradesh .
- It flows through Baghelkhand ,Palamu,Magadha .
- It joins with Ganges at Patna in the state of Bihar.
- The flood plain of Son river is very narrow.
- The Indrapuri Barrage and Bansagar Dam is built along this river .
- Koilwar Bridge is located across this river.
4.PunPun river
- It originates from Chota Nagpur plateau at Palamu district in the state of Jharkhand.
- It joins with Ganges at Fatuha in the state of Bihar.
5.Phalgu River
The river Phalgu is formed by confluence of two rivers Lilajan and Mohana rivers near Gaya in Bihar state.
6.Kiul River .
This river flows through the state of Jharkhand.
7.Karmanasa River
- This river originates in Kaimur Range .
- It flows through the states of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar .
- This river flows through Rohtas Plateau in the state of Bihar.
8.Chandan River
This river flows through the state of Bihar.
Hooghly River

Fig : Howrah Bridge
- It is the distributary of Ganga river..
- The Ganga river splits into Padma and the Hooghly river near Guria in Murshidabad .
- Padma flows eastward through Bangladesh whereas Hooghly flows through West Bengal.
- The upper riparian zone of this river is known Bhagirathi and lower zone is Hooghly.
- Major rivers drain into Hooghly includes Ajay, Rupnarayan ,Haldi ,Damodar etc.
